User manual
►Minimum requirements
►Users
There are 2 user types
Guest: As a guest you don't have to use a username and a password. You can access HNC with the following limitations:
- You can't save subcorpus sets. Searches are either performed on the whole HNC corpus or on the selected set during the current session.
- Search results are always limited to 5 sentences max.
- In "Statistics", only the top 100 most frequent words/lemmas are available.
Registered user: For full HNC access, you must be a registered user. During your registration you will be asked for a username and a password which are strictly personal. As a registered user you have the right to:
- Perform searches on the whole HNC corpus but also on any subcorpus set you have selected.
- Perform searches on subsets you have created and saved in the past.
- Perform searches on words, lemmas or parts of speech.
- Use the Word Analysis and Correlation of Words Tool.
- Retrieve up to 5000 sentences.
►Document selection
As a Guest, you have no right to save a subcorpus set and perform searches with previously created ones. Searches are performed either in HNC as a whole or in the subcorpus set created during the current version.
As a registered user you can perform searches both in HNC as a whole and in previously saved subcorpus sets based on user classification filters. (Figure 1)
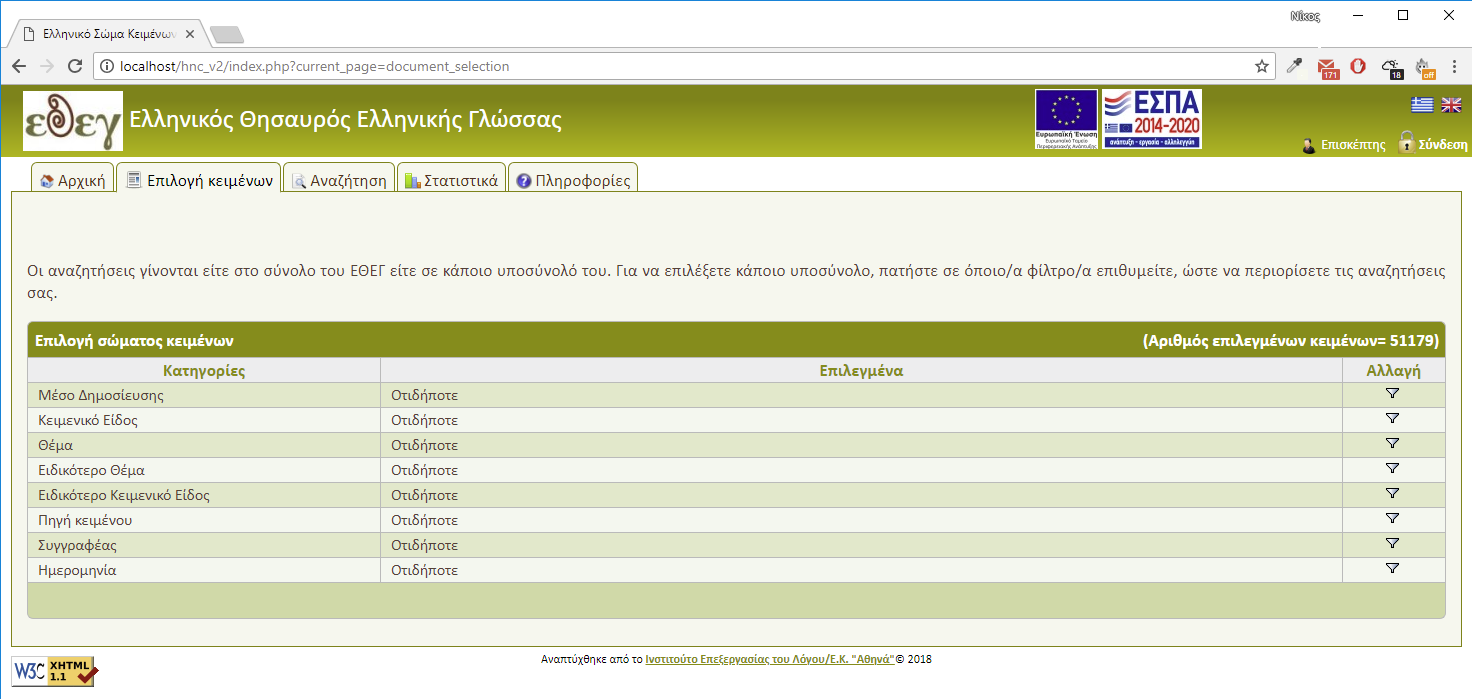
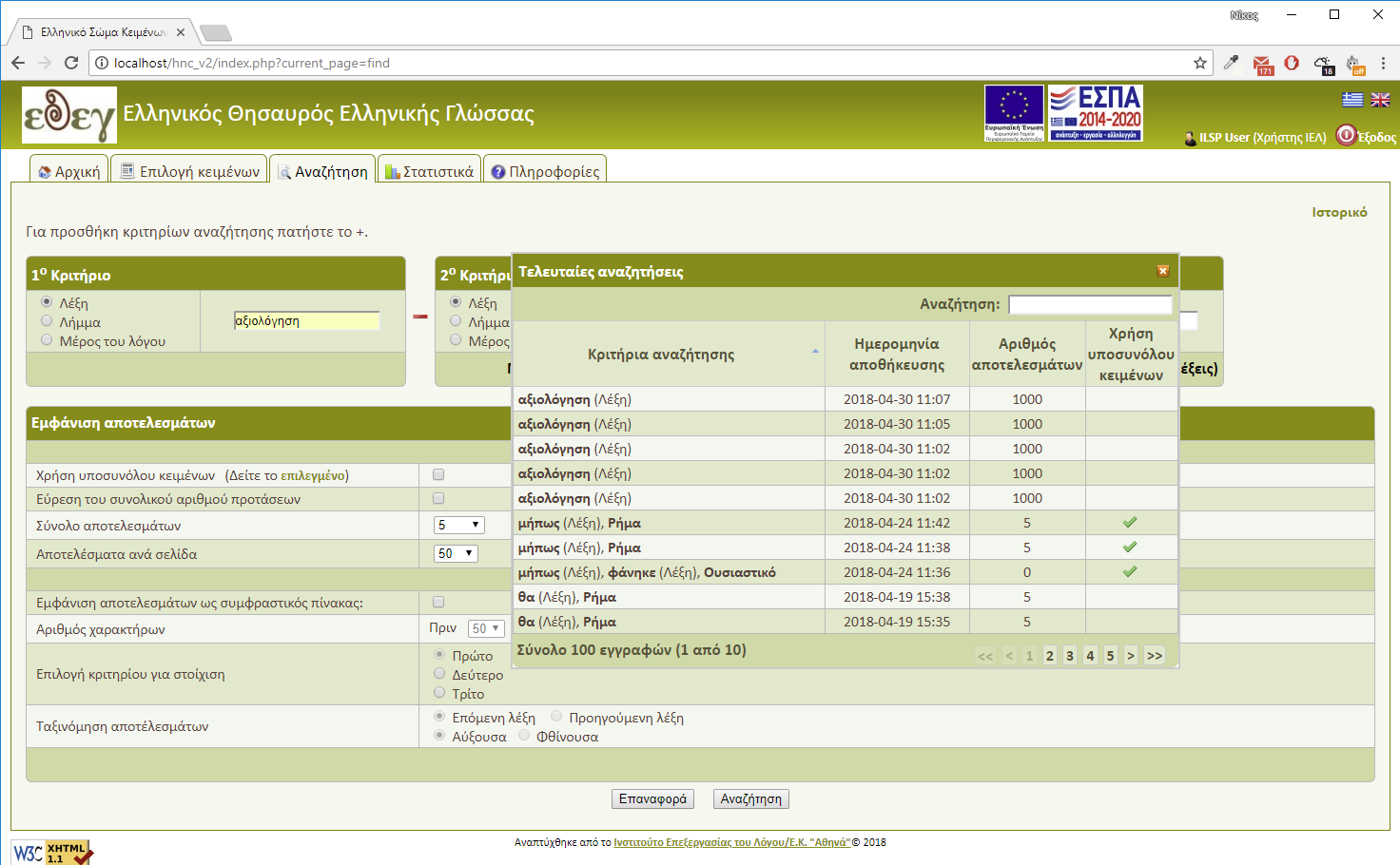
If you create a subcorpus set, it is automatically saved. Therefore, you can use it in other sessions.
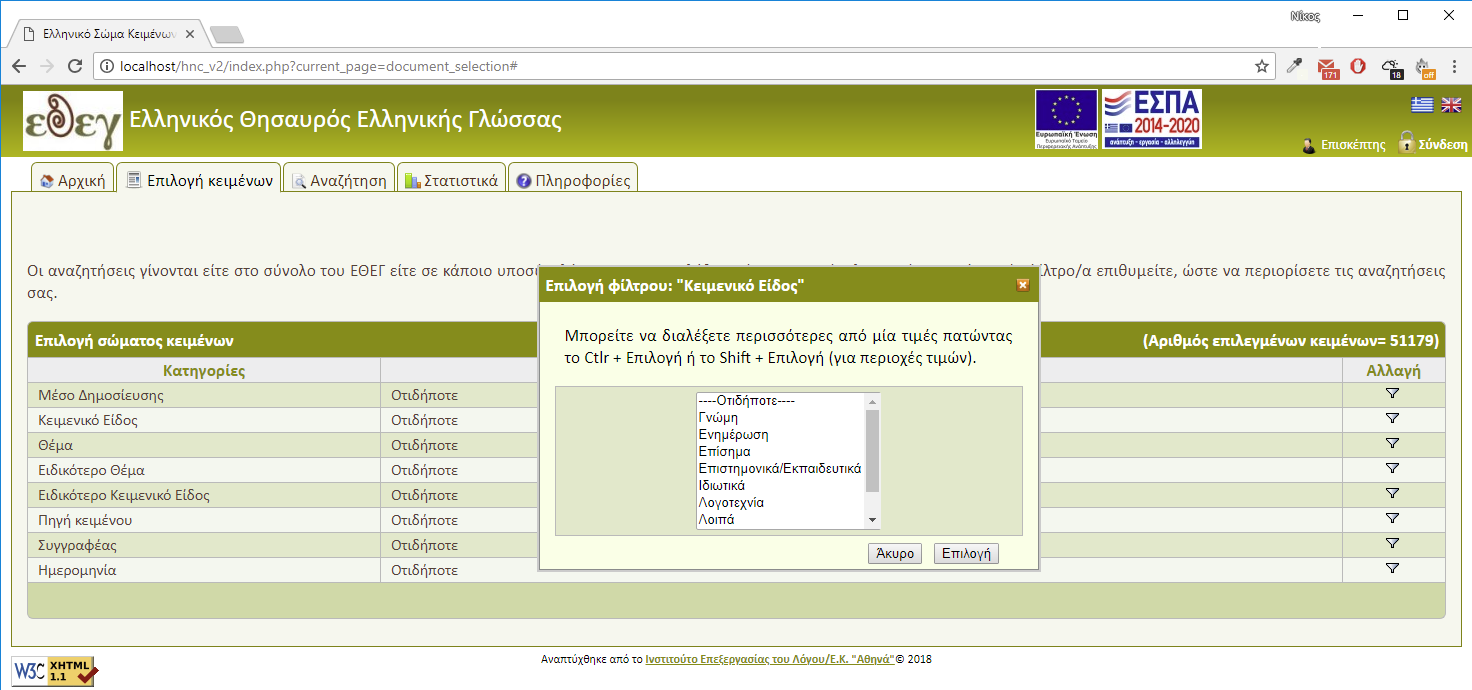
In Document selection (Figure 2), A category is selected as a filter and then filter values are picked. Multiple values can be selected by pressing
- Button Shift + value (for selecting successive values) or
- Button Ctrl + value (for selecting non successive values).
The same procedure can be repeated for any number of filters. Filter selection process can be cancelled at any moment by pressing the 'Cancel' button at the value selection window or by just closing the window. After completing the document selection, you can proceed to sentence search. You don't have to store the subcorpus set during your current connection because it is automatically saved. In case you want to keep it for future use you can save it manually and then load it from your profile page. (Figure 3)
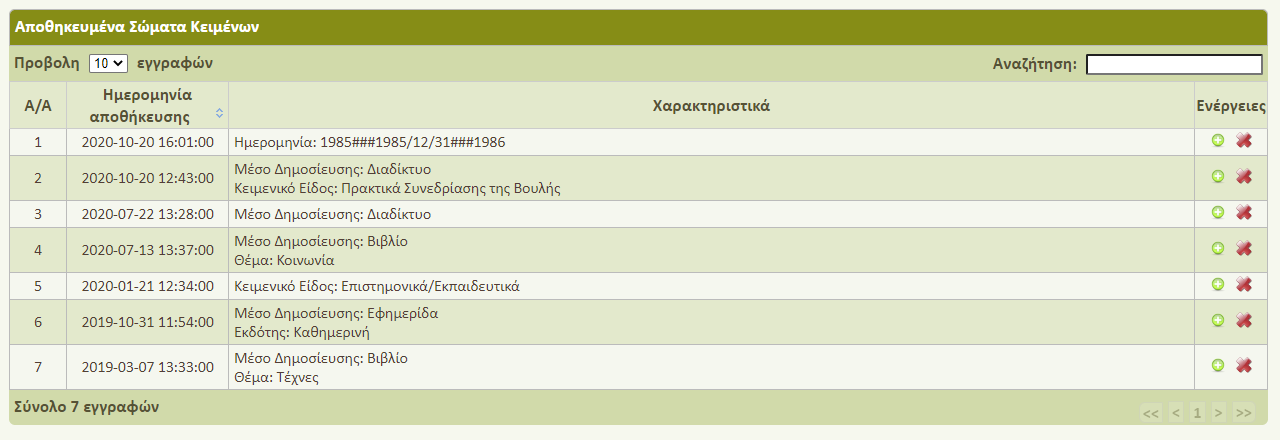
►Sentence search
System's functionality is as follows: you can pose the system with certain types of searches and the system responds by retrieving sentences that satisfy the criteria selected by the user (Figure 3). Search queries contain from 1 to 3 criteria and you can add or remove search criteria by pressing the + or - icon button (Figure 5).
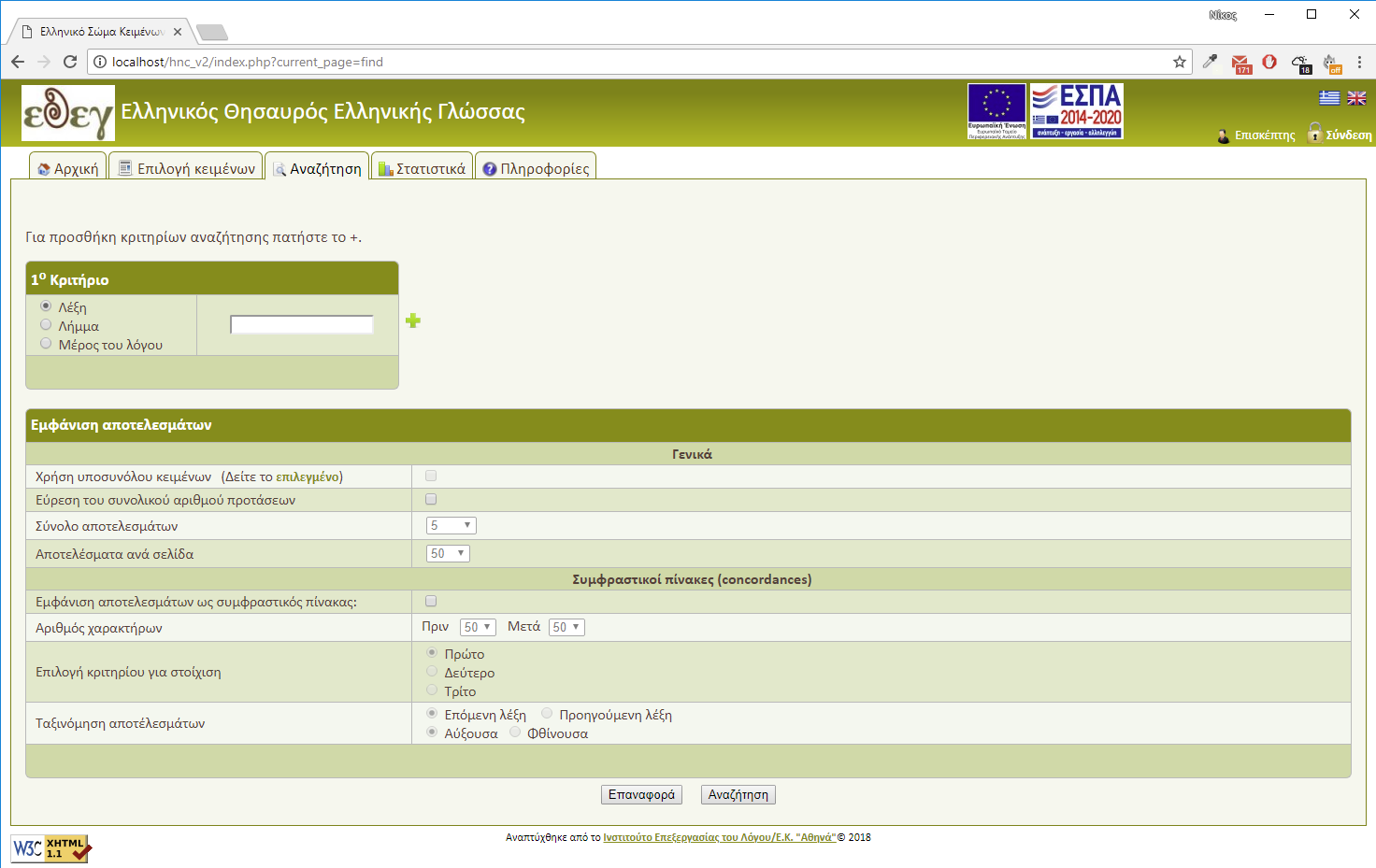
- Searches can be performed for: words, lemmas and parts of speech (or combinations of those three criteria, therefore you can look for:
- specific words: when searching for the word "παίζω", all sentences containing this word are retrieved
- lemmas (a lemma is the basic form of a word as it appears in learner's dictionaries; it is an abstract entity and represents all word forms: when searching for the lemma "παίζω", sentences containing various word forms of the specific lemma will be retrieved from HNC such as "παίζει", "παίξει", "παίζοντας",
- grammatical definitions (i.e. parts of speech and their morhological features): when searching for "noun" all sentences containing nouns are retrieved, and their combinations (e.g. word-lemma, word -grammatical definition, word-lemma-grammatical definition)
- You have to use stresses where needed, but words or lemmas are case insensitive.
- You can select the maximum distance between two criteria e.g. Pronoun [ maximum distance 3 ] κάνω [ maximum distance 2 ] Noun
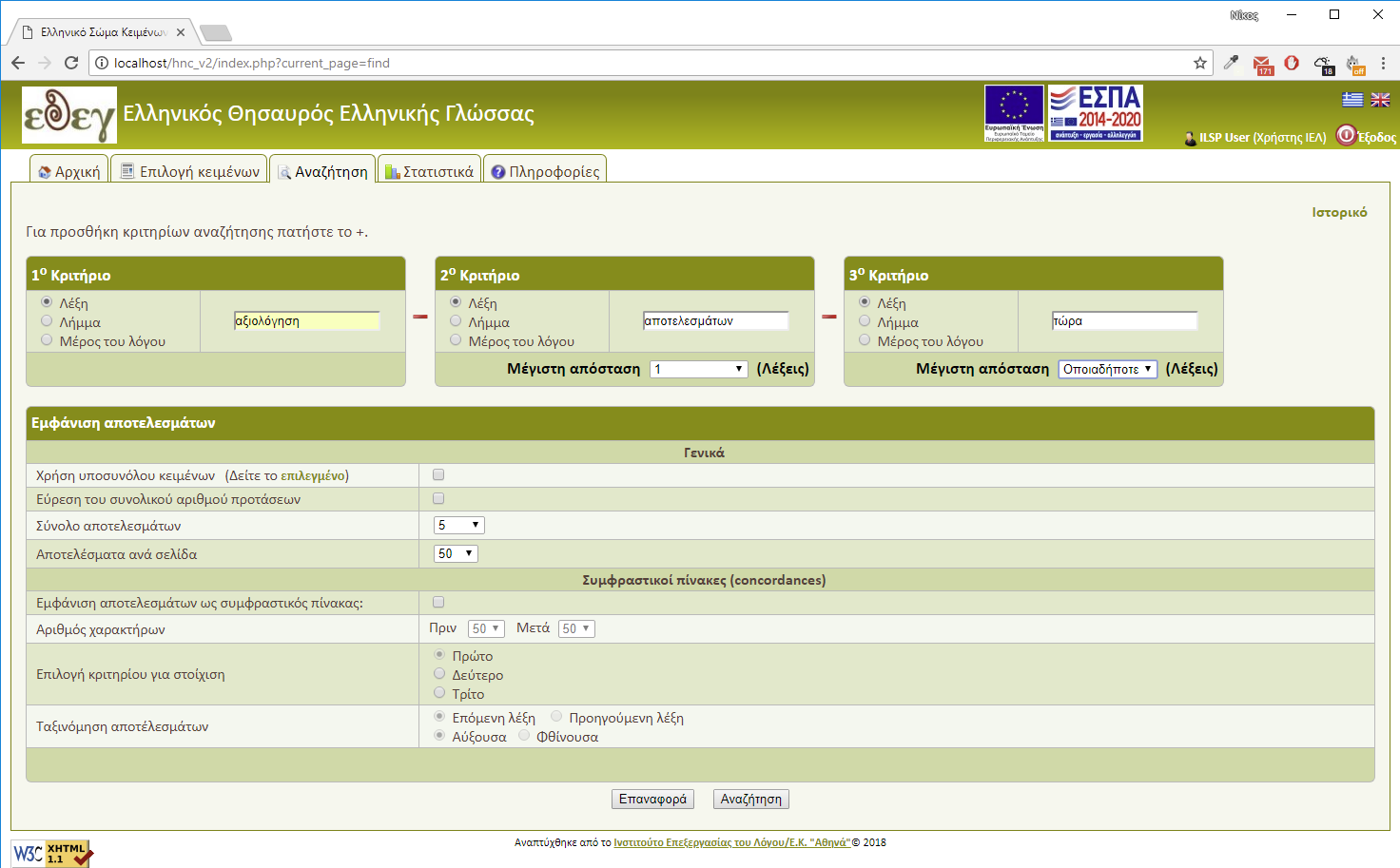
Based on the maximum distance selection 3 between the first and second word, the system will retrieve as a result sentences, where words may have a distance between 1 and 3 words (Fig. 4)
- You can set the maximum number of sentences that will be retrieved and also the maximum number of sentences per result page.
- Wildcard characters can also be used in case of word or lemma criteria.
To replace only one character, the user must use '_' character, (underscore) while for more than one characters '%' (percentage) can be used.
Examples:
- ακαδημαϊκο_ (all words beginning from the string "ακαδημαϊκο" and include one more letter)
- ακαδη% (all words begining from the string "ακαδη"),
- %μαϊκός (all words ending with the string "μαϊκός"),
- %δημα% (all words including the string "δημα"). - For each criterion, whether it is a word or a lemma, you can use the logical operators OR (|) and NOT (|^).
Examples:
- αυγό|αβγό (Resulting sentences will contain any of the words αυγό or αβγό)
- πέν_|^πένα|^πέντ% (Resulting sentences will contain words that start with the string "πέν" but words "πένα" and those that start with "πέντ" will be excluded)
►Search results
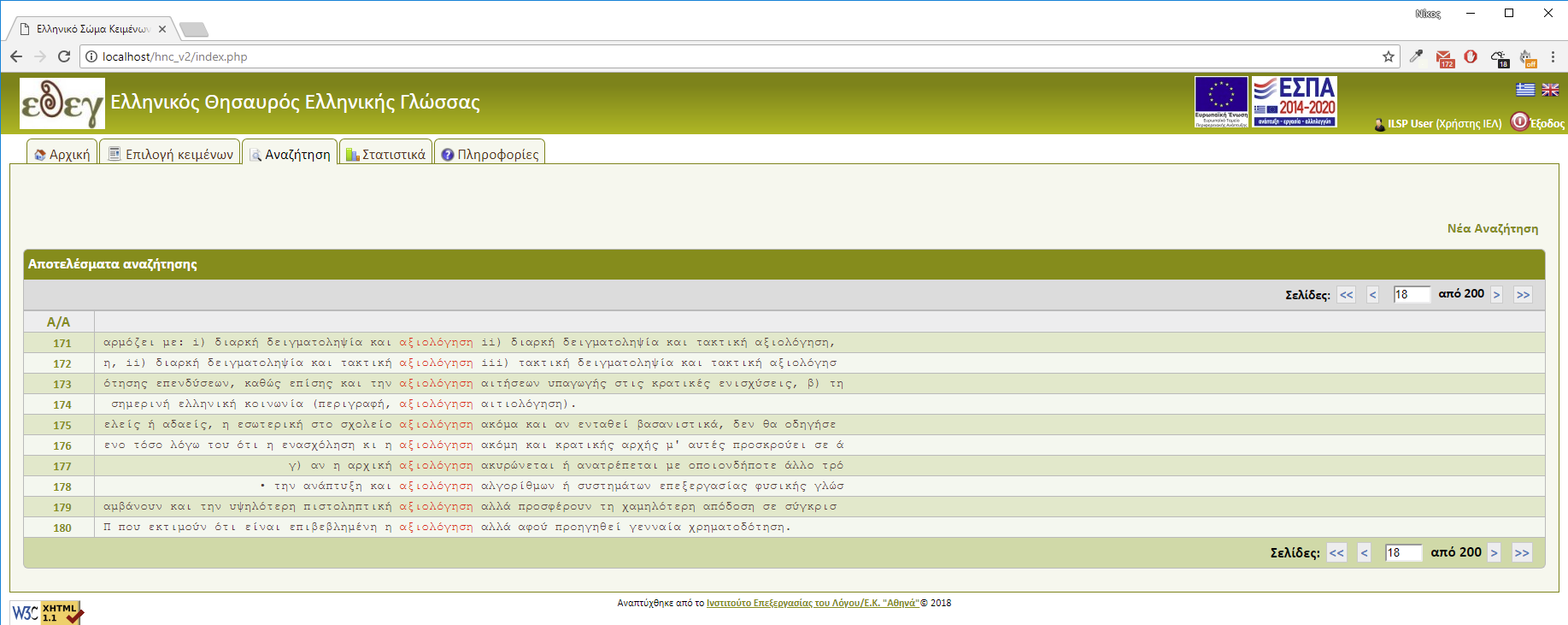
Search results for a guest cannot be more than 5 sentences. Search results for a subscriber can reach the total of 5000 sentences (Figure 7).
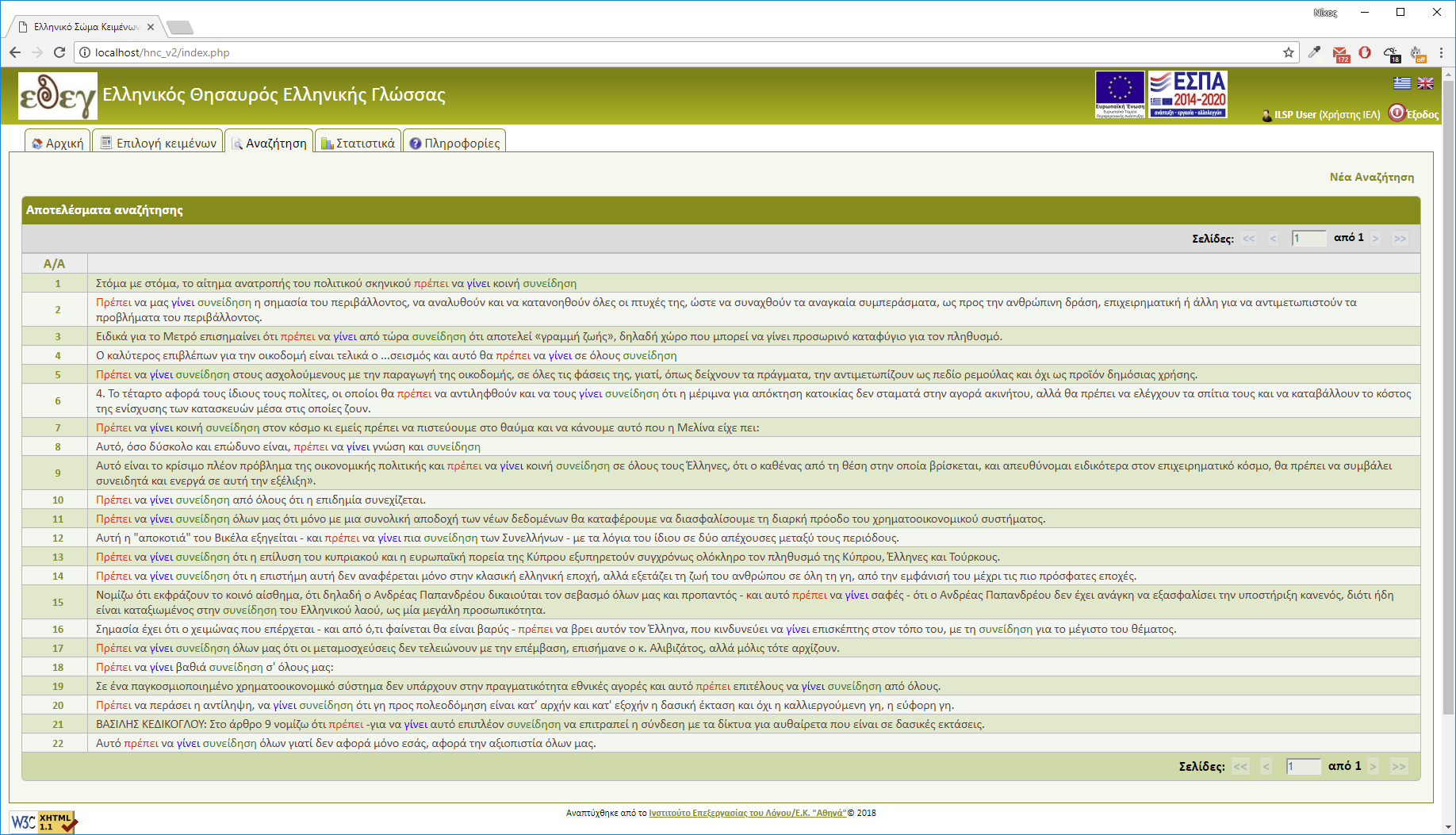
- A search result is a list of sentences without a strictly set order.
- Results are numbered. Each number is a link providing all document info in which the sentence was found. To return to the search list you can close the popup window.
►Concordances
HNC Corpus provides the functionality of displaying retrieved sentences in concordance tables. For this display mode, the user must select which criterion will be used for word alignment, sorting of sentences according to the word following or preceding the alignment word, and the number of characters displayed before and after the alignment criterion (Figure 8)
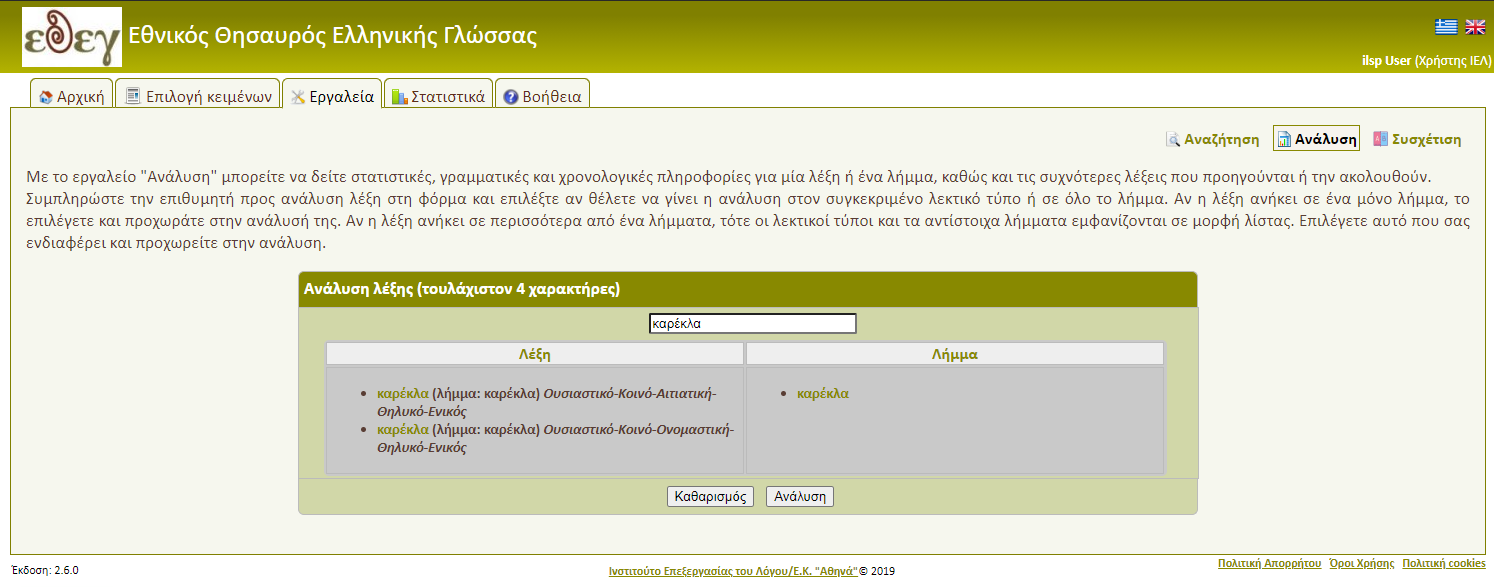
►Word Analysis
The user can use the Analysis tool to see the statistical, grammatical and chronological information of a word or lemma, as well as the most frequent words preceding or following. Users submit the preferred word into the analysis form. If the word corresponds to more than one lemma then the user has to select the desired one from the list appearing below by clicking on it. (Figure 9).
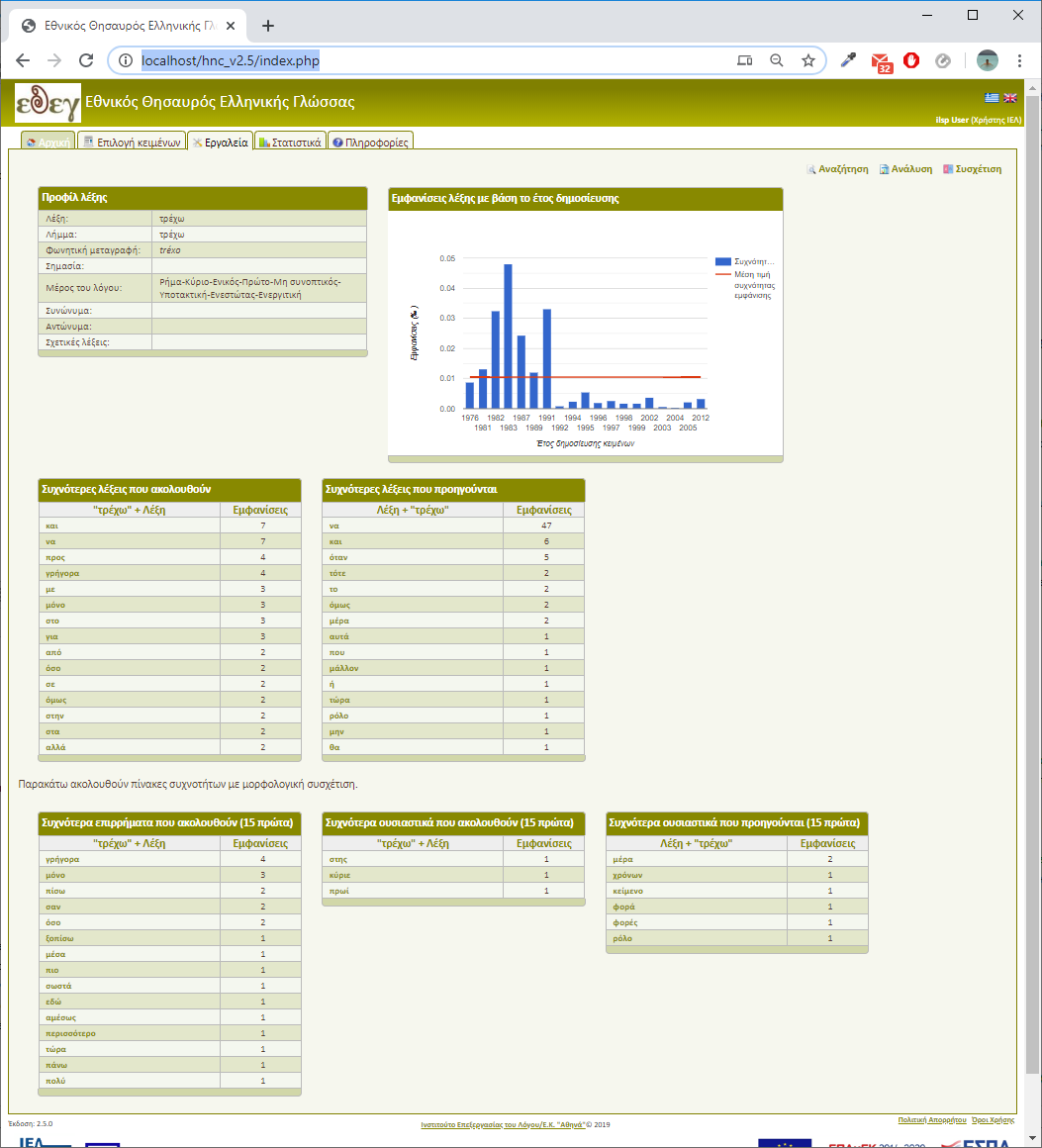
HNC presents a word analysis in multiple panels (Figure 10). Word's linguistic profile appears in the above left panel. Right beside, word appearances in relevance with the publication year.
The second row presents occurrence tables of words preceding or following the selected word. Finally, according to the grammatical category of the selected word, tables of occurrences of preceding or following words of specific grammatical types are presented.
►Correlation of words
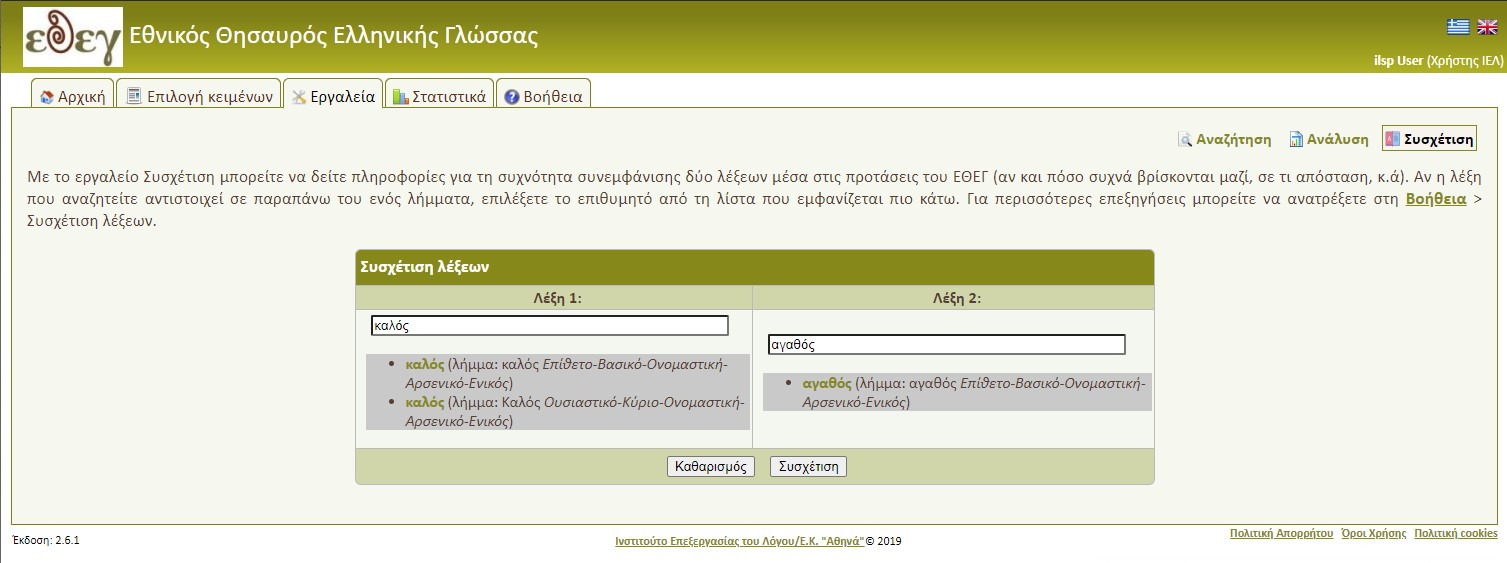
"Correlation" tool will return the correlation result (Figure 12, Figure 13) that includes:
- The occurrence table of each word in isolation in a sentence and in specific grammatical combinations according to their part of speech.
- The correlation by distance table that presents co-occurrences and their distribution according to the selected word distance.
- The bar diagram of word co-occurrence in relation to the year of publication.
- The highest co-occurrence table of words following or preceding the first word and their corresponding occurrences of same words following or preceding the second word.
- Finally if the pair of words has the same part of speech, then tables of bigger co-occurrence combinations of first word with other specific grammatical categories are presented and in comparison to the same combination occurrences for the second word.
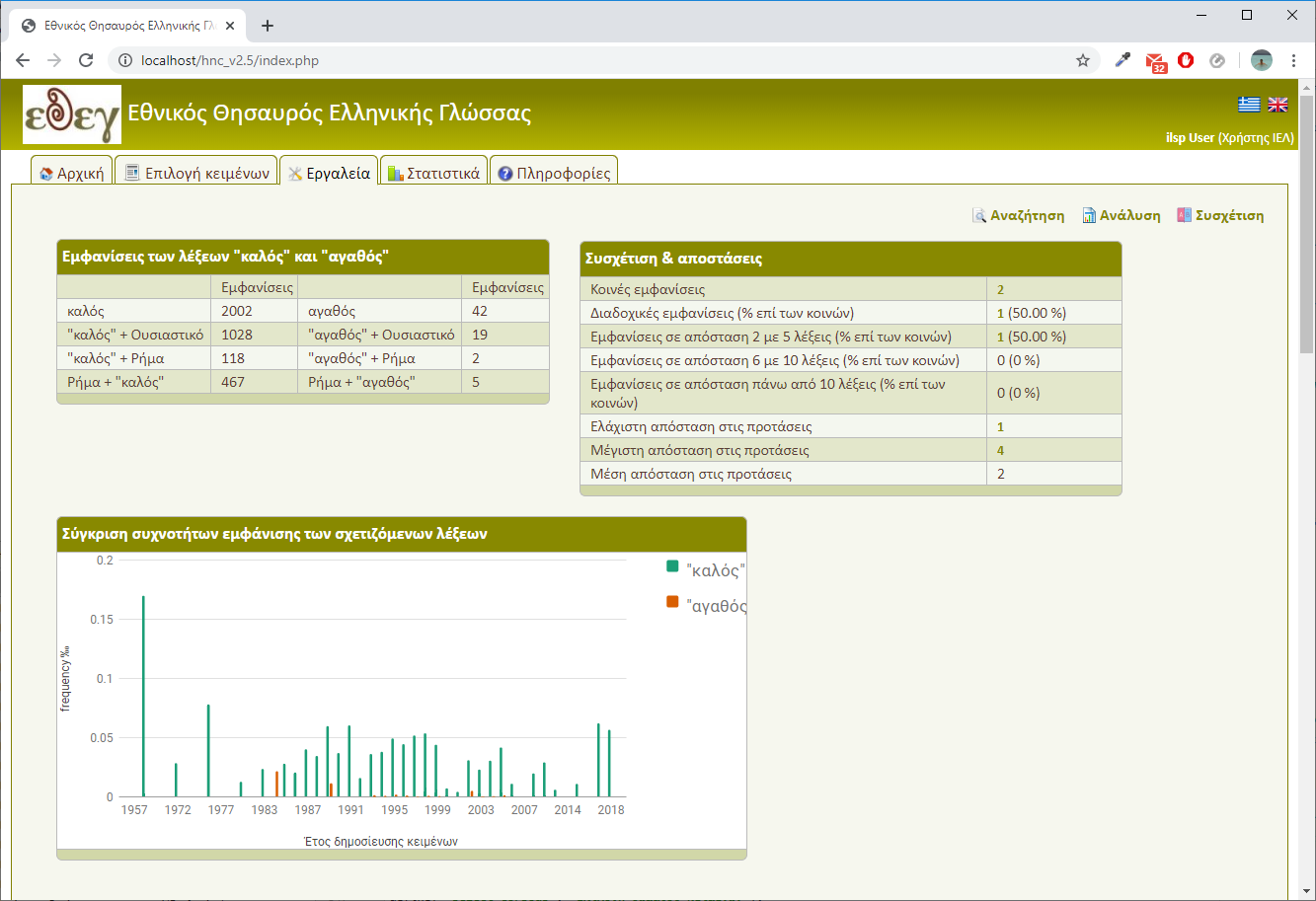
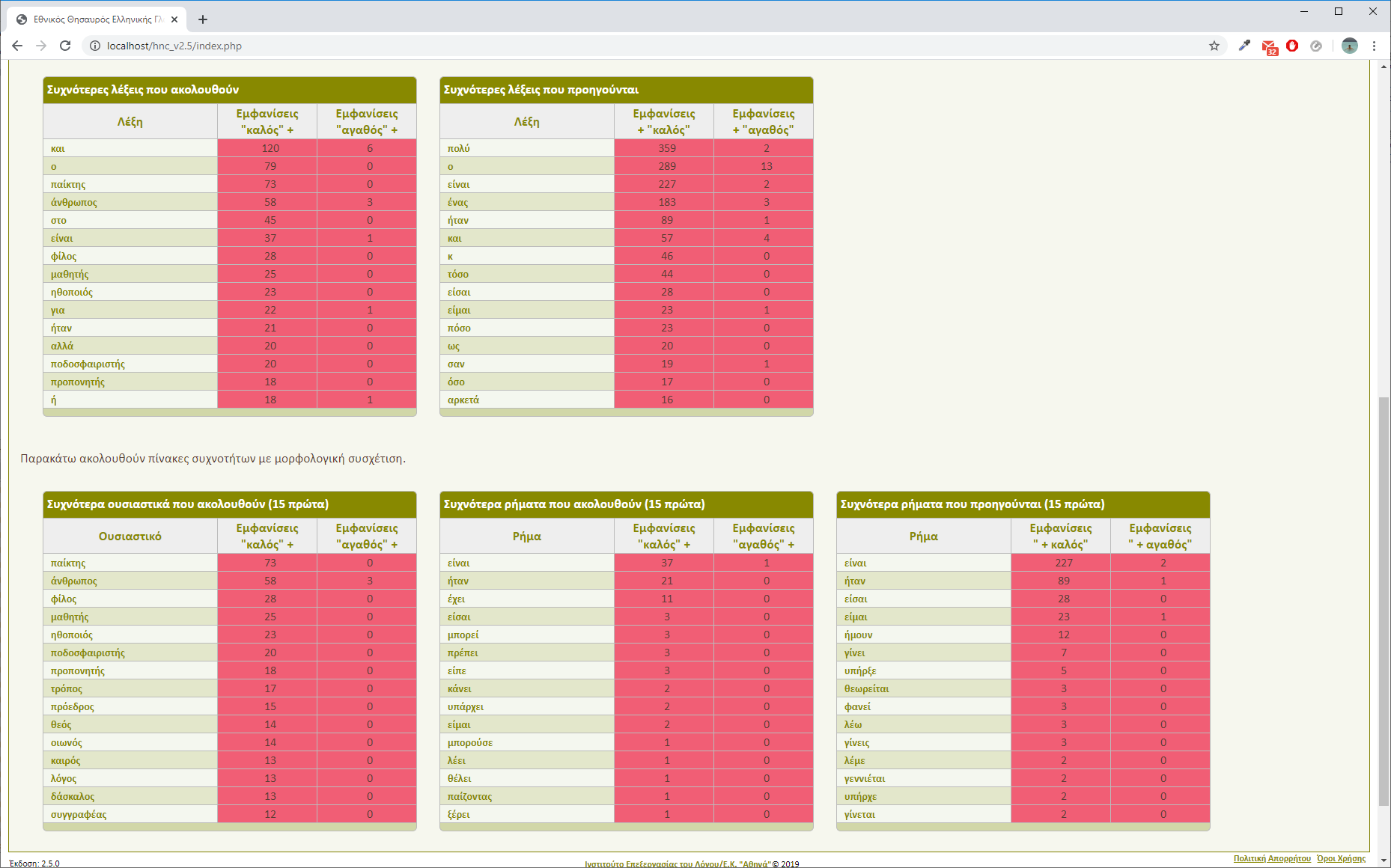
Cell colouring indicates the following::
- Dark rose -> Big superiority in terms of occurrences in correlation with first word over the second.
- No colouring -> No superiority in terms of occurrences in correlation with first word over the second.
- Dark blue -> Big superiority in terms of occurrences in correlation with second word over the first.
►Statistics
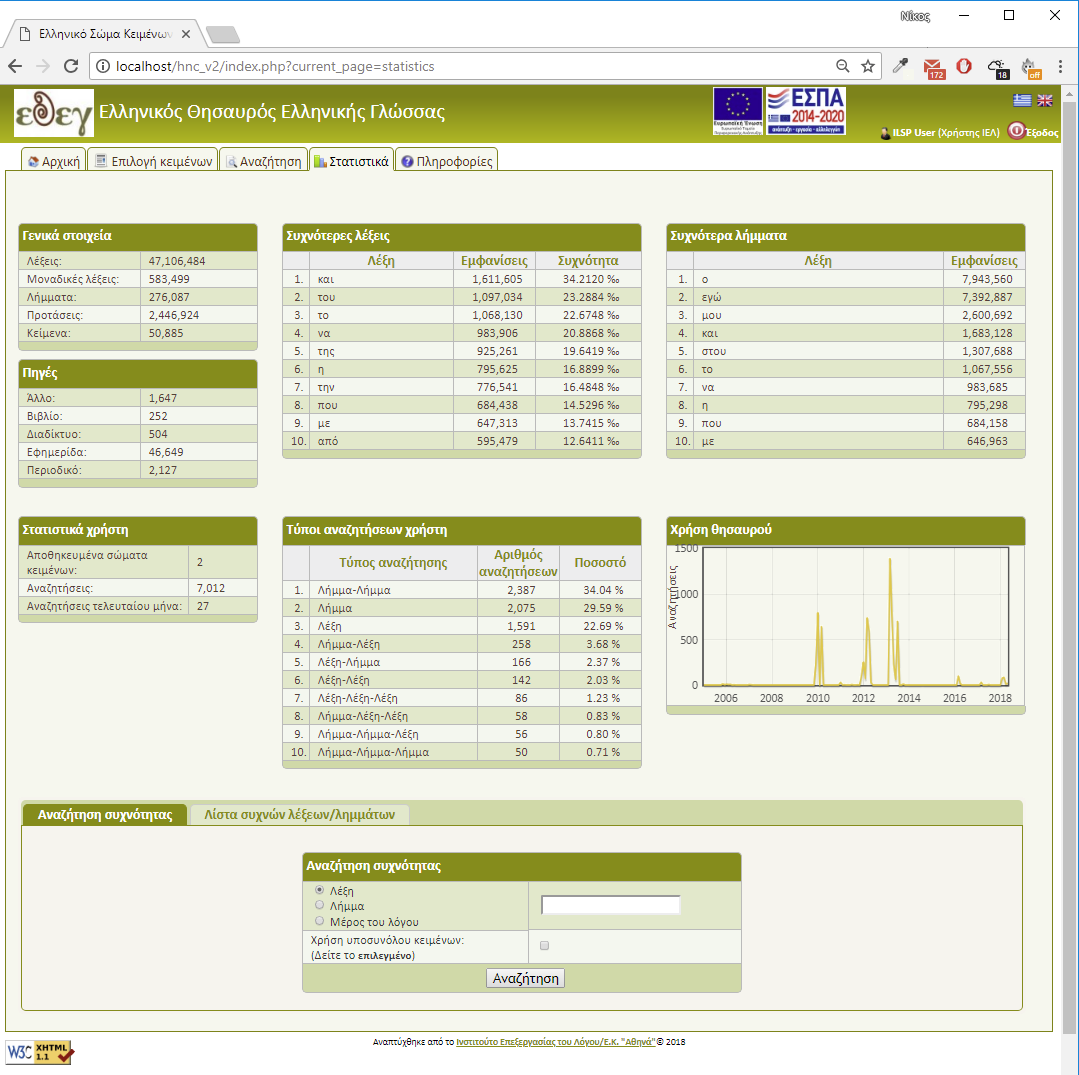
The user can see HNC statistical data in the "Statistics" menu tab. (Figure 14) The statistics include:
- General information about HNC (total number of words, texts etc., number of texts per publication medium)
- A list with the 10 most frequent words and lemmas in HNC
- Statistical information about user searches
- Frequency search of specific words or lemmas. For the statistical data the user can use special characters, as mentioned above in Word Search.
- The list of the most frequent word or lemmas in HNC (up to 2000 results).
 Hellenic National Corpus (HNC)™
Hellenic National Corpus (HNC)™

 Login
Login Sign-in
Sign-in Home
Home Document selection
Document selection Search
Search Statistics
Statistics Help
Help Manual
Manual Info
Info Sources
Sources


 Profile
Profile Exit
Exit